Squids are Cephalopods in the order Teuthida, which has
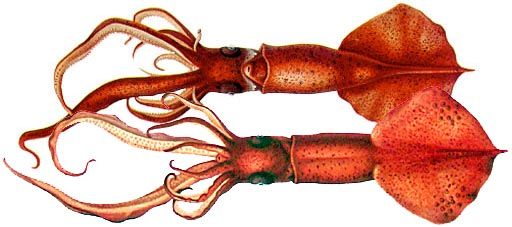
about 304 species. Like all Cephalopods, squids have a head, arms, bilaterally symmetrical, fins, and mantle. Like cuttlefish squids have 8 arms arranged in pairs of two, most of the time longer. Squids are strong swimmers, some can even `fly` through the water doing a long glide or propels themselves through the water fast.
Squids are in the class Cephalopoda, subclass Coleoidea, and order Teuthida, which has two major suborders, Myopsina and Oegopsina. Teuthida is the biggest cephalopod order including 300 species and 29 families.
The order Teuthida is a member of the suborder Decapodiformes (in Greek meaning `ten legs`). Two other orders of Decapodiformes cephalopods are squids, recognizable for their long slimy arms and elongated body. They are bobtail squids in the order Sepiolida and the rams horn squid Spirulida. The vampire squid is more related to octopuses than squids.
Members of Cephalopoda:
Nautiloids: nautiluses
Ammonoidea: Ammonites
Belemnoidea: extinct belemnoids
Spirulida: ram`s horn squid
Sepiida: cuttlefish
Sepiolida: bobtail squids
Teuthida: squid
Octopoda: octopus
Vampyromorphida: vampire squid
Loliginidae: inshore, calamari, grass squid
Ancistrocheiridae: sharpear enope squid
Architeuthidae: giant squid
Batoteuthidae: bush-club squid
Chtenopterygidae: comb-finned squids
Cranchiidae: glass squids
Gonatiae: armhook squid
Histioteuthidae: jewel squid
Joubiniteuthidae: Joubin`s squid
Lepidoteuthidae: Grimaldi scaled squid
Magnapinnidae: bigfin squid
Mastigoteuthidae: whip-lash squid
Ommastrephidae: flying squid



 Polychaete worms are scale worms found in marine habitats. These worms are sometimes called 'bristle worms' because they often bear spines. These worms can be found in small rivers, all the way to the deepest depths of the ocean, as in the Challenger Deep expedition, a small 2-3cm polychaete worm was found right at the bottom of the Mariana trench. There are more than 100,000 species of polychaete worms. Common representatives of polychaete worms are the lugworm, sandworm, and clamworm. Only 2% (168 species) of the polychaetes are found in fresh water. Polychaetes range in size from 2cm to 3m.
Polychaete worms are scale worms found in marine habitats. These worms are sometimes called 'bristle worms' because they often bear spines. These worms can be found in small rivers, all the way to the deepest depths of the ocean, as in the Challenger Deep expedition, a small 2-3cm polychaete worm was found right at the bottom of the Mariana trench. There are more than 100,000 species of polychaete worms. Common representatives of polychaete worms are the lugworm, sandworm, and clamworm. Only 2% (168 species) of the polychaetes are found in fresh water. Polychaetes range in size from 2cm to 3m. 







